Wind power is the conversion wind energy into a useful energy source such as electricity. Wind turbines use an electrical generator grid to convert the electrical current produced by the rotations of the wind turbine blades then transferred into gear box, from gear box it will turn the generator and produce DC electricity, which can be further converted into an alternating current(AC).
Wind energy is actually produced by the sun. the energy from the sun hitting the earth’s surface will converted into wind energy. This conversion happens because of a phenomena called “differential heating” which is a result of the many different types of landscapes and water ways, heating and cooling at different rates causing a global atmospheric convection system.
in this earth, wind rises from the equator and moves north and south in the higher layers of the atmosphere, The region of Earth receiving the Sun's direct rays is the equator. Here, air is heated and rises, leaving low pressure areas behind. Moving to about thirty degrees north and south of the equator, the warm air from the equator begins to cool and sink. Between thirty degrees latitude and the equator, most of the cooling sinking air moves back to the equator. The rest of the air flows toward the poles
to learn more about this see at http://winds-energy.blogspot.com/2007/03/geographical-variation-in-wind-resource.html
picture below also give good visualization of global wind direction in earth 
Wind Distributions in our World
before calculating the exact number or think that your want to builds wind turbine in your area, first let's look same fact date circulation of global wind, and wind speed distributions in our worlds.
United States Annual Average Wind Turbine 
Maps of mean 80-m wind speeds for year 2000
from this map we can get detail information of wind power in each countries.
Europe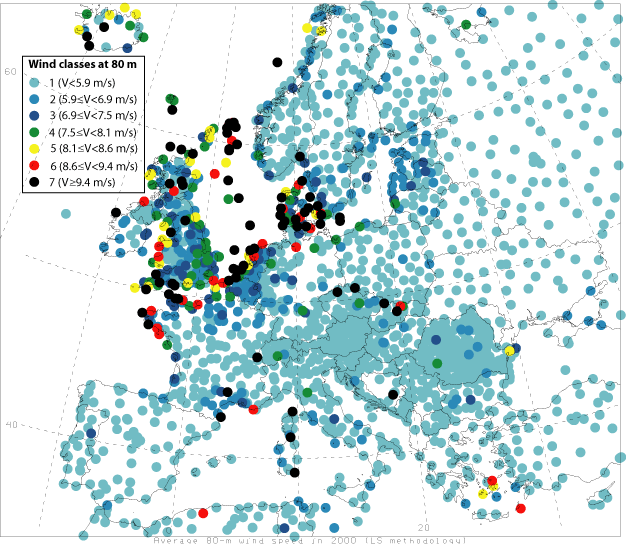
North America
South America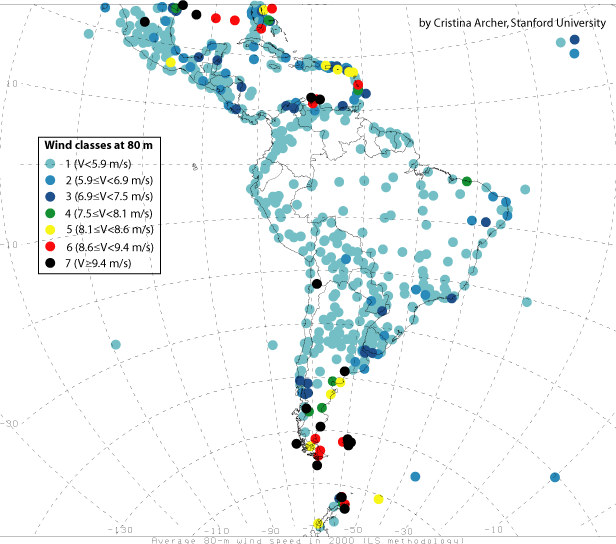
Asia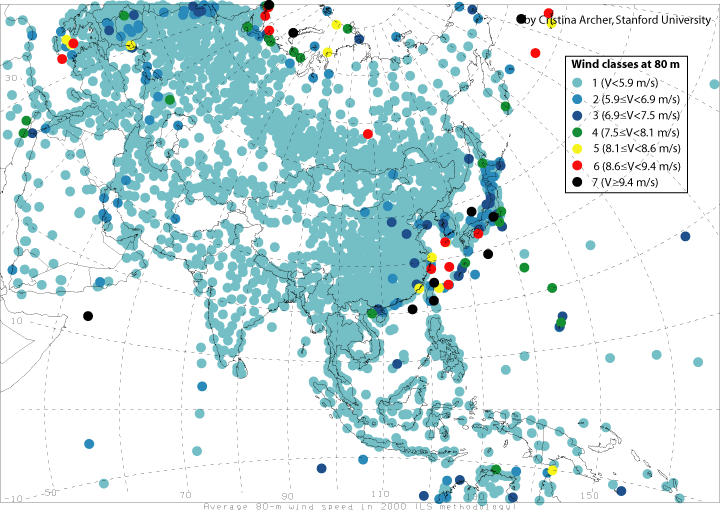
Australia
Africa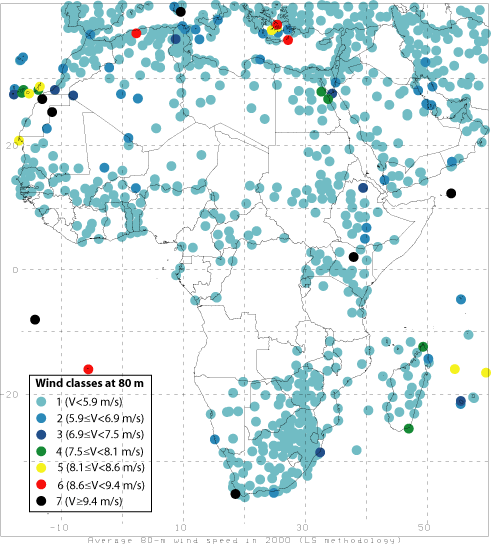
Conclusion and Summary
1. Approximately 13% of all stations worldwide belong to class 3 or greater (i.e., annual mean wind speed ≥ 6.9 m/s at 80 m) and are therefore suitable for wind power generation.
2. Sub tropical Countries have more good potential wind energy than tropical countries.
3.Offshore stations experience mean wind speeds at 80 m that are ~90% greater than over land on average.
References
http://www.etopiamedia.net/emeenn/pages/wpw/wpw2-5551212.html
http://www.windstuffnow.com/main/wind_charts.htm
http://www.clemson.edu/scies/wind/Poster-Schmidt.pdf
Global Winds and Wind Distributions in Worlds and many continents
Posted by hasnan | 5:16 AM | Global winds, map of wind, wind distributions | 0 comments »Vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWT)
Posted by hasnan | 8:49 AM | VAWT, Vertical-axis wind turbines | 4 comments »Vertical-axis wind turbines (VAWT) are a type of wind turbine where the main rotor shaft runs vertically. VAWTs work somewhat like a classical water wheel in which water arrives at a right angle (perpendicular) to the rotational axis (shaft) of the water wheel. Vertical-axis wind turbines fall into two major categories: Darrieus turbines and Savonius turbines.
Savonius Turbine
invented in Finland, the Savonius turbine is S-shaped if viewed from above. This drag-type VAWT turns relatively slowly, but can produce a high torque. It is useful for grinding grain, pumping water and other works that need high torque, but if this kind of turbine connected with electric generator, it only can produce a little electricity
picture below shown schematics Savonius Turbine
The commonest VAWT is a Savonius VAWT which is an extended version of an anemometer (wind speed measuring tool). VAWTs can offer up to 15% efficiency and they work equally well no matter which direction the wind is coming from.
Darrieus wind turbine
A Darrieus machine, a VAWT, is a vertical axis wind turbine. It acts much like a windmill except that a windmill has a horizontal axis
Darrieus wind turbines are not self-starting. Therefore a small powered motor is required to start off the rotation, and then when it has enough speed the wind passing across the aerofoils starts to generate torque and the rotor is driven around by the wind.
In overall comparison, while there are some advantages in Darrieus design there are many more disadvantages, especially with bigger machines in MW class. The Darrieus design uses much more expensive material in blades while most of the blade is too near of ground to give any real power.
others type that derivaties from Darrieus wind turbine are
The giromill was included in Darrieus's 1927 patent for vertical aerofoil powered vertical axis wind turbines, however development is now starting again on new giromills which take advantage of modern ultra strong light materials to produce turbine blades robust enough to cope with the stresses they are put under.
Another variation of the Giromill is the Cycloturbine, in which the blades are mounted so they can rotate around their vertical axis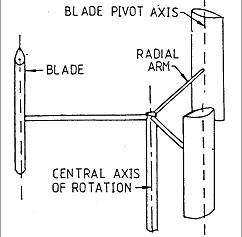
below is interesting concept for callobaration between Darrieus and Savonius 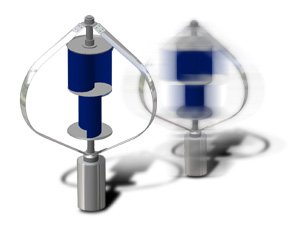
Wind Power Conversion Systems with MERS
Posted by hasnan | 4:12 AM | construction, Conversion system, MERS | 0 comments »innovative power conversion technology using magnetic energy recovery switch (MERS), they are two type of MERS that available in market,
1. conventional wind power conversion,
A variable speed synchronous generator
with many poles is connected to a grid through an ac-dc converter and a dc-ac inverter, see the picture below 
The disadvantage of this conventional conversation system is that an output voltage of the synchronous generator will decreases with the increase of current
because of synchronous reactance. Since the overload capacity of generator is small, an instantaneous strong wind power energy cannot be taken out and it is not efficient.
2. Diode Rectifier in Mers
this system actually still in development process in Tokyo institute of technology,
is a wind power conversion system with MERS with diode rectifier second picture above can improve a power factor regardless of the impedance and power frequency of the load, and it ca generates voltage and compensates for the synchronous reactance voltage. furthermore, the output voltage of the generator will increases, and it becomes possible to improve limited output power and efficiency of the wind
power system. Therefore, it is expected that the efficiency improvement of the power conversion system and the miniaturization of wind turbine generator can be expected. Moreover, the MERS works as ac breaker.
Growth Annual Installed capacity of Wind Turbine
Posted by hasnan | 3:28 AM | wind turbin installed, wind turbine growth | 0 comments »Wind is simple air in motion. It is caused by the uneven heating of the earth’s surface by the sun then the earth’s surface is made of very different types of land and water, it absorbs the sun’s heat at different rates.
Today global wind power capacity rose 27 percent in 2007 to more than 94,100 megawatts, led by capacity additions in the European Union, the United States, and China.
Brussels, 6 February 2008. The Global Wind Energy Council today confirmed its earlier estimate that over 20,000 MW of wind power was installed in 2007, led by the US, China and Spain, bringing world-wide installed capacity to 94,123 MW. This is an increase of 31% compared with the 2006 market, and represents an overall increase in global installed capacity of about 27%.
The top five countries in terms of installed capacity are Germany (22.3 GW), the US (16.8 GW), Spain (15.1 GW), India (8 GW) and China (6.1 GW). In terms of economic value, the global wind market in 2007 was worth about 25bn EUR or 36bn US$ in new generating equipment.
The market for European wind power capacity broke new records in 2006, according to the annual statistics issued by the European Wind Energy Association (EWEA) today. 7,588 MW of wind power capacity, worth some €9 billion, was installed last year in the EU, an increase of 23% compared to 2005.
Europe is leading Wind Turbine Capacity
from total of growth installed capacity of wind Europe is leading with about 75 % total installed 
Installed capacity of Wind Turbine in USA
U.S. wind energy installations now exceed 10,000 megawatts (MW) in generating capacity, and produce enough electricity on a typical day to power the equivalent of over 2.5 million homes, the American Wind Energy Association (AWEA) announced today. A megawatt of wind power generates enough to serve 250 to 300 average homes.(http://www.awea.org/newsroom/releases/US_Wind_Energy_Installations_Milestone_081006.html)
International ranking of Wind Turbine
The strong position of China, and even more of India (home of manufacturer Suzlon, which has just won the battle to buy German manufacturer Repower, and purchased Belgian gearbox subcontractor Hansen last year) should be noted.
The American Wind Energy Association (AWEA) reported last week record growth in wind power generation with 5,244 megawatts of capacity installed in 2007 – a 45% increasereflecting $9 billion in investment and 30% of all new power generating capacity in 2007
Cost and Economic Of Wind Energy
Posted by hasnan | 8:41 PM | Cost wind energy, Economic of Wind Energy | 0 comments »Based on Report from FPL Energy, As of January 2007, the company's wind-power portfolio consists of more than 4,000 net megawatts, and the largest U.S. generator of wind power, with 47 wind farms currently in 15 states.
Today, wind energy is also the fastest growing clean and renewable energy resource in the world. American Wind Energy Association report write that
* global installed capacity is more than 74,000 megawatts
* U.S. installed capacity is more than 11,600 megawatts.
Wind Energy Cost
In the early 1980's, when the first utility-scale wind turbines were installed, wind-generated electricity cost as much as 30 cents per kilowatt-hour. Now, state-of-the-art wind power plants at excellent sites are generating electricity at less than 5 cents/kWh. Costs are continuing to decline as more and larger plants are built and advanced technology is introduced.
The main parameters governing wind power economics
include the following:
・Investment costs, including auxiliary costs for foundation, grid-connection, and so on.
・Operation and Maintenance (O&M) costs.
・Electricity production/average wind speed.
・Turbine lifetime.
・Discount rate.
There is no Such Thing as a Single Price for Wind Energy
annual electricity production will vary enormously depending on the amount of wind on your turbine site. Therefore, there is not a single price for wind energy, but a range of prices, depending on wind speeds.
graph below shown the sample of electric cost of Wind Energy

Turbine Cost is Banana Cost
Based on The Danish Wind Industry Association (DWIA) prices vary for each generator size. The reasons are e.g. different tower heights, and different rotor diameters. One extra metre of tower will cost you roughly 1 500 USD. A special low wind machine with a relatively large rotor diameter will be more expensive than a high wind machine with a small rotor diameter.
here some fact data of Economic Wind Energy

